Tethers Unlimited, Inc. (TUI) announced it has completed delivery of 15 S-band Software Defined Radios (SDR) in support of a smallsat constellation mission being developed by Millennium Space Systems, a Boeing Company.
TUI delivered all 15 radios on schedule, demonstrating success in its efforts to stand up a radio production line capable of meeting the aggressive timelines of small satellite constellation program. The deliveries also included the first small satellite mesh networking solution to support inter-satellite data transfer.
The SWIFT-SLX radio is a compact, affordable software defined radio designed to provide S-band and L-band communications for small satellites. Its suite of “software defined apps” make it readily configurable to support a wide range of mission needs, from aviation to cislunar missions. TUI supports a wide range of band frequencies and makes an effort to work with the customer to meet their requirements. The SWIFT-SLX SDR has 11 units flying in LEO orbit and several dozen more in the launch pipeline.
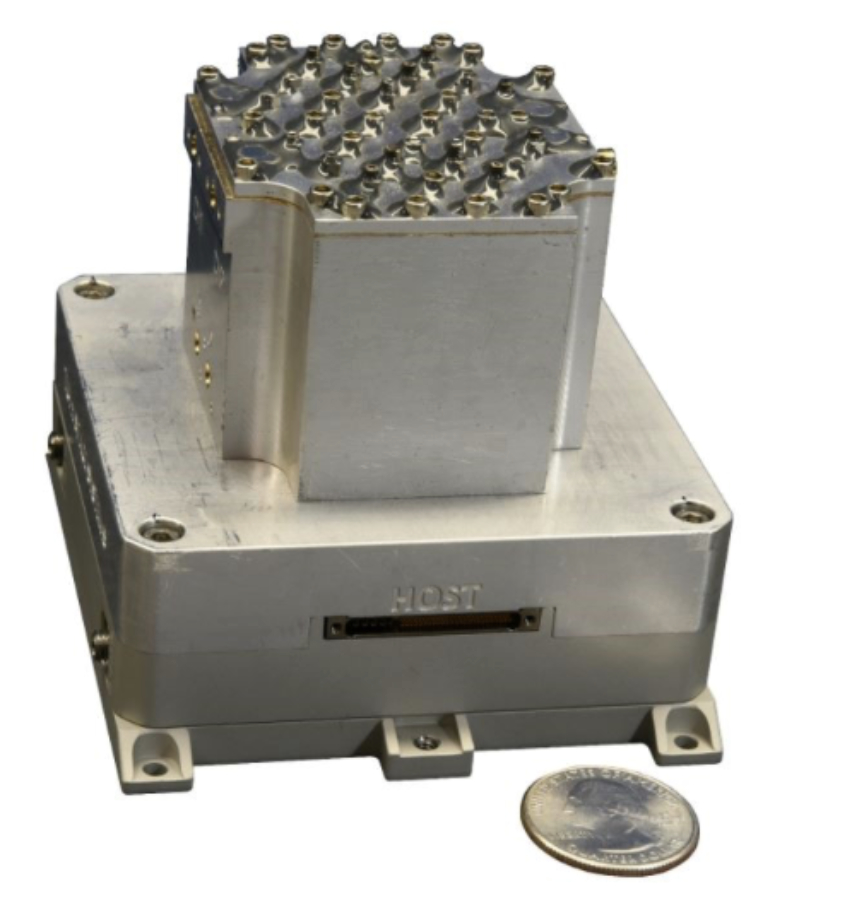

Tether’s Unlimited’s SWIFT-SLX SDR.
TUI has had a long-standing partnership on advanced space technologies with Millennium dating back over a decade.

Dr. Robert Hoyt
“Hitting this delivery rate has taken substantial investments in automating our radio testing infrastructure,” said Dr. Rob Hoyt, TUI’s President. “The space industry has traditionally focused on producing satellite components one at a time, and there wasn’t much experience in the industry with mass production. We’ve brought in experts in lean production from outside the space industry, and that has paid off in a transformation of our radio manufacturing capability.”
“The culture of collaboration and teamwork between both Millennium Space Systems and Tethers Unlimited has contributed to this and many other past successes.” said Seckin Secilmis, TUI’s COO.
Recent Tethers Unlimited news…
Tethers Unlimited to Participate in NASA’s PUNCH Mission
AMERGINT Holdings Tethers … Through Acquisition … Tethers Unlimited
Space Networking Solution for Smallsats Unveiled by Tethers Unlimited